Seafile, a Self-Hosted Dropbox Alternative¶
Last updated: May 2022. For advanced users. Solid tech skills required.
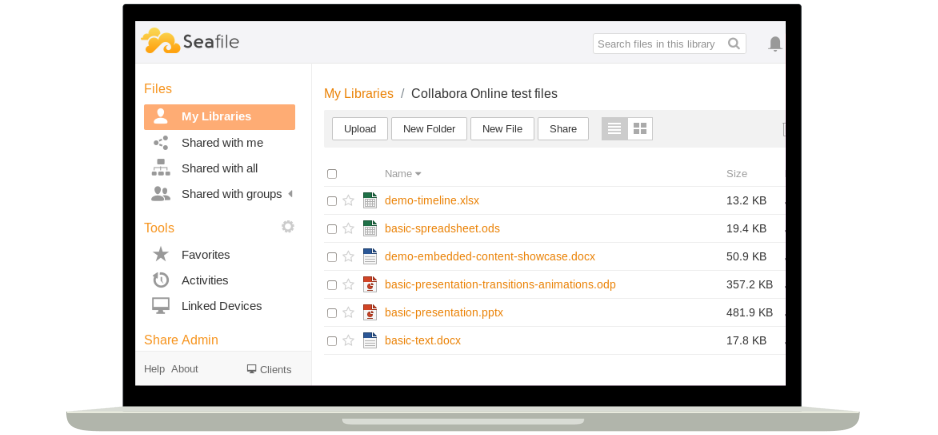
Looking to sync files across your devices and share them with family and friends? Seafile is a self-hosted file hosting service for your home server! It doesn't boast a wide array of features, but excels at keeping your files synchronised across multiple devices, and supports encryption. Seafile is free, open source, fast and reliable. By making use of delta sync, Seafile only synchronises updated or changed file chunks, rather than entire files. You can access your home cloud storage from clients for various platforms, including mobile devices.
What about Nextcloud or Syncthing?
Nextcloud is a popular and feature-rich file sync solution. It's FOSS and offers many additional features such as contact management, video conferencing, web mail, calendars, and so on. On the downside, file syncing is comparatively slow.
Syncthing is a decentralized file sync solution. It's FOSS, and contrary to Seafile and Nextcloud, there is no need for a central server or database. On the downside, file syncing can be comparatively slow and, depending on your network setup, you might run into firewall issues.
Can't I just use my current cloud storage?
Sure, if you trust commercial cloud providers with your private data. Despite their claims, cloud solutions such as iCloud, GDrive, Dropbox, or OneDrive keep copies of the keys protecting your privacy, can access your data or provide it to third parties.
| Cloud provider | Privacy policy extracts |
|---|---|
| Apple iCloud | “Messages in iCloud also uses end-to-end encryption. If you have iCloud Backup turned on, your backup includes a copy of the key protecting your Messages. This ensures you can recover your Messages if you lose access to iCloud Keychain and your trusted devices.“ |
| Google Drive & WhatsApp | “Media and messages you back up aren't protected by WhatsApp end-to-end encryption while in Google Drive.“ |
| Dropbox | “To provide these and other features, Dropbox accesses, stores, and scans Your Stuff. You give us permission to do those things, and this permission extends to our affiliates and trusted third parties we work with.” |
| Microsoft OneDrive | “When you use OneDrive, we collect data about your usage of the service, as well as the content you store, to provide, improve, and protect the services. Examples include indexing the contents of your OneDrive documents so that you can search for them later and using location information to enable you to search for photos based on where the photo was taken.” |

Database preparation¶
Seafile can be deployed with different databases, including MySQL, SQLite, PostgreSQL and so on. In this tutorial, we'll generate MySQL databases required by Seafile's server components. Read on below for detailed instructions.
Show me the step-by-step guide
Log into the server and create a system user which will run Seafile. For the purpose of this tutorial, we'll call this system user seafileadmin. Of course, you can choose any name, just make sure to adjust the commands accordingly:
sudo adduser --disabled-login seafileadmin
Log into MySQL as root with the following command:
sudo mysql -u root -p
Run the command below to create the MySQL user seafileadmin (adjust accordingly). Make sure to replace the string StrongPassword with a strong, unique password:
CREATE USER 'seafileadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'StrongPassword';
Next, generate databases required by Seafile and grant correct permissions:
CREATE DATABASE ccnet;
CREATE DATABASE seafile;
CREATE DATABASE seahub;
GRANT ALL ON ccnet.* TO 'seafileadmin'@'localhost';
GRANT ALL ON seafile.* TO 'seafileadmin'@'localhost';
GRANT ALL ON seahub.* TO 'seafileadmin'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
Log back into MySQL as the user seafileadmin (adjust accordingly):
sudo mysql -u seafileadmin -p
Make sure all databases have been created correctly:
SHOW DATABASES;
The output should look similar to this:
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| ccnet |
| seafile |
| seahub |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Exit MySQL:
EXIT;
Show me the 1-minute summary video
Error during creation of Seafile admin
Several users reported issues when trying to install Seafile on a Ubuntu Server. The issue seems to be related to MySQL 8, which uses caching_sha2_password as default authentication plugin. This is being solved by creating the MySQL user seafileadmin with the authentication plugin mysql_native_password, as described in the section above.

How to install Seafile¶
Follow the instructions below to resolve all dependencies and install Seafile on your Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Show me the step-by-step guide
Prerequisites¶
Seafile requires Python to run, install it on the server:
sudo apt install python3 python3-{setuptools,pip} libmysqlclient-dev memcached libmemcached-dev libffi-dev
Next, deploy additional packages as the seafileadmin user (adjust accordingly):
sudo -H -u seafileadmin pip3 install --user django==3.2.* Pillow pylibmc captcha jinja2 sqlalchemy==1.4.3 django-pylibmc django-simple-captcha python3-ldap mysqlclient pycryptodome==3.12.0
Installation script¶
Check the latest release of Seafile's Server for Linux. At the time of writing, it was 9.0.5. Download and decompress the package with the following commands (adjust the version number accordingly):
sudo wget -4 https://download.seadrive.org/seafile-server_9.0.5_x86-64.tar.gz
sudo tar -xvf seafile-server_*
sudo mkdir /var/www/seafile
sudo mkdir /var/www/seafile/installed
sudo mv seafile-server-* /var/www/seafile
sudo mv seafile-server_* /var/www/seafile/installed
Temporary workaround for Ubuntu 22.04
At the time of writing, Seafile 9.0.5 doesn't support the 1.15.0 version of the cffi module, which comes bundled with Ubuntu 22.04. For this reason, it hasn't been deployed together with the other Python modules in the previous step. Instead, we'll apply a temporary workaround. After setting the right permissions for the seafileadmin user (adjust accordingly), we'll install version 1.14.6 of the cffi module in the thirdpart folder:
sudo chown -R seafileadmin:seafileadmin /var/www/seafile
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/seafile
sudo -H -u seafileadmin pip3 install --force-reinstall --upgrade --target /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-9.0.5/seahub/thirdpart cffi==1.14.6
Run the installation script:
sudo bash /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-9.0.5/setup-seafile-mysql.sh
Follow the on-screen instructions:
| Instruction | Description |
|---|---|
| Server name | Choose a name for the Seafile server. For the purpose of this tutorial, we'll choose gofoss_seafile, adjust accordingly. |
| Domain | Provide the domain name used by the cloud storage. It's the same address as the web interface we'll set up later on. For the purpose of this tutorial, we'll choose https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org, adjust accordingly. |
| Port | Choose the TCP port used by Seafile. The default value is 8082. |
| Databases | Use the existing ccnet/seafile/seahub databases, which were created previously. |
| Host of MySQL server | The default value is localhost. |
| Port of MySQL server | The default value is 3306. |
| MySQL user | Provide the name of the MySQL user. In our example, that's seafileadmin, adjust accordingly. |
| Password of MySQL user | Provide the password of the MySQL user. |
| ccnet database name | Provide the name of the ccnet database. In this case, it's ccnet. |
| seafile database name | Provide the name of the seafile database. In this case, it's seafile. |
| seahub database name | Provide the name of the seahub database. In this case, it's seahub. |
After successful installation, the terminal should display something like:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Your seafile server configuration has been finished successfully.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
run seafile server: ./seafile.sh { start | stop | restart }
run seahub server: ./seahub.sh { start <port> | stop | restart <port> }
-----------------------------------------------------------------
If you are behind a firewall, remember to allow input/output of these tcp ports:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
port of seafile fileserver: 8082
port of seahub: 8000
When problems occur, refer to https://download.seafile.com/published/seafile-manual/home.md for information.
Show me the 1-minute summary video

Setting up the home cloud storage¶
After successfully installing Seafile, we're going to configure a number of settings such as language preferences, permissions and administrator accounts, auto start at boot and so on. More details below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
Language¶
Change the language preferences. In this example, we'll use English:
echo "export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8" >>~/.bashrc
echo "export LANG=en_US.UTF-8" >>~/.bashrc
echo "export LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8" >>~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
Make sure the settings have been applied correctly with the following command:
locale
The terminal should display something similar to:
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_NUMERIC="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TIME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_COLLATE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MONETARY="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MESSAGES="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_PAPER="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_NAME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ADDRESS="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TELEPHONE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MEASUREMENT="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_IDENTIFICATION="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
Of course, you can configure any other language. Check which languages (or "locales") the server currently supports:
locale -a
If you want to add other languages, edit the following configuration file by removing comments from the required lines (for example es_ES.UTF-8 for Spanish, fr_FR.UTF-8 for French, nl_NL.UTF-8 for Dutch, and so on):
sudo vi /etc/locale.gen
Apply the changes:
sudo locale-gen
Now run the commands presented in the section above, applying your preferred language settings.
Administrator account¶
Set the right permissions and switch to the /var/www/seafile directory:
sudo chown -R seafileadmin:seafileadmin /var/www/seafile
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/seafile
sudo chmod 750 /home/seafileadmin
cd /var/www/seafile
Start Seafile:
sudo -H -u seafileadmin bash -C '/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seafile.sh' start
Start Seahub:
sudo -H -u seafileadmin bash -C '/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh' start
The first time Seahub starts, it will ask to set up an administrator account. For the purpose of this tutorial, we'll provide the administrator email seafileadmin@gofoss.net. Of course, any other suitable email address will do. Just make sure to adapt the relevant commands accordingly. When prompted, provide a strong, unique password.
Auto start¶
Let's make sure Seafile automatically starts every time the server boots. Create a first configuration file:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/seafile.service
Add the following content:
[Unit]
Description=Seafile
After= mysql.service network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seafile.sh start
ExecStop=/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seafile.sh stop
User=seafileadmin
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file (:wq!), then create a second configuration file:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/seahub.service
Add the following content:
[Unit]
Description=Seahub
After= mysql.service network.target seafile.service
[Service]
Type=forking
Environment="LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8"
ExecStart=/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh start
ExecStop=/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh stop
User=seafileadmin
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file (:wq!).
Autostart Seafile at each boot:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable seafile
sudo systemctl enable seahub
Reboot the server:
sudo reboot
Make sure Seafile is up and running (the status should be "Active"):
sudo systemctl status seafile
sudo systemctl status seahub
Wrap up¶
The cloud storage will be accessible from a domain of your choice. For the purpose of this tutorial, we'll choose https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org. Of course, any other suitable address will do. Just make sure to adapt the relevant commands accordingly. Open the first configuration file:
sudo vi /var/www/seafile/conf/seahub_settings.py
Make sure the SERVICE__URL is pointing to the right address:
SERVICE_URL = "https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org/"
Then, add the following lines at the end of the file (adapt the time zone and URL according to your own setup):
TIME_ZONE = 'Europe/Budapest'
SESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSE = True
LOGIN_ATTEMPT_LIMIT = 2
FILE_SERVER_ROOT = 'https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org/seafhttp'
Save and close the file (:wq!).
Show me the 2-minute summary video

Web interface¶
We are going to set up an Apache Virtual Host as a Reverse Proxy to access Seafile's web interface. Read on below for more details on how to set this up.
Show me the step-by-step guide
Create an Apache configuration file:
sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org.conf
Add the following content and make sure to adjust the settings to your own setup, such as domain names (myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org), path to SSL keys, IP addresses and so on:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org
ServerAlias www.myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org
Redirect permanent / https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org
ServerAlias www.myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org
ServerSignature Off
SecRuleEngine Off
SSLEngine On
SSLProxyEngine On
SSLProxyCheckPeerCN Off
SSLCertificateFile /etc/dehydrated/certs/gofoss.duckdns.org/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/dehydrated/certs/gofoss.duckdns.org/privkey.pem
DocumentRoot /var/www/seafile
<Location />
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Allow from 127.0.0.1
Allow from 192.168.1.0/24
Allow from 10.8.0.1/24
</Location>
Alias /media /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seahub/media
RewriteEngine On
<Location /media>
Require all granted
</Location>
# seafile fileserver
ProxyPass /seafhttp http://127.0.0.1:8082
ProxyPassReverse /seafhttp http://127.0.0.1:8082
# seahub
SetEnvIf Authorization "(.*)" HTTP_AUTHORIZATION=$1
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass / http://127.0.0.1:8000/
ProxyPassReverse / http://127.0.0.1:8000/
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org-error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Once the content is added, save and close the file (:wq!).
Note how we enable SSL encryption for Seafile with the instruction SSLEngine On, and use the SSL certicate /etc/dehydrated/certs/gofoss.duckdns.org/fullchain.pem as well as the private SSL key /etc/dehydrated/certs/gofoss.duckdns.org/privkey.pem, which were created earlier on.
Also note how we disabled ModSecurity in the Apache configuration file with the instruction SecRuleEngine Off, as Seafile and ModSecurity don't play well together.
Next, enable the Apache Virtual Host and reload Apache:
sudo a2ensite myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org.conf
sudo systemctl reload apache2
Configure Pi-Hole to resolve Seafile's local address. Browse to https://mypihole.gofoss.duckdns.org and log into Pi-Hole's web interface (adjust accordingly). Navigate to the menu entry Local DNS Records and add the following domain/IP combination (adjust accordingly):
DOMAIN: myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org
IP ADDRESS: 192.168.1.100
Browse to https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org and log in as seafileadmin@gofoss.net (adjust accordingly). Then apply the following settings:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| System Admin ‣ Settings | Change the field SERVICE_URL to https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org and click on Save. |
| System Admin ‣ Settings | Change the field FILE_SERVER_ROOT to https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org/seafhttp and click on Save. |
Show me the 2-minute summary video

File sharing apps¶
Seahub¶
Seahub isn't really a client, but Seafile's web interface. Users can log in from a browser and navigate through folders, upload, edit & download files, share data with others, and so on. Seahub natively displays file formats from Microsoft and LibreOffice, as well as videos, pictures, pdf & text files, and many more. Changes applied via Seahub are mirrored across all synced devices.
Syncing client¶
This client keeps selected files & folders in sync across connected devices. It's best suited for devices with sufficient storage capacity.
Show me the step-by-step guide for Windows
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Installation | Download & install the latest release of Seafile's Desktop Sync Client for Windows.  |
| Storage | Launch the Seafile client and select a local folder to be synched with the cloud. 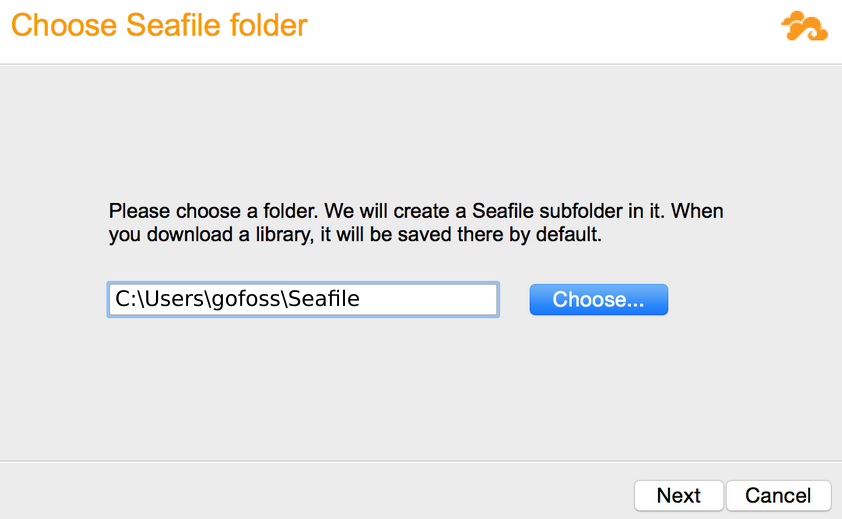 |
| Credentials | Provide the server name as well as user credentials. If enabled, also provide two-factor authentication. 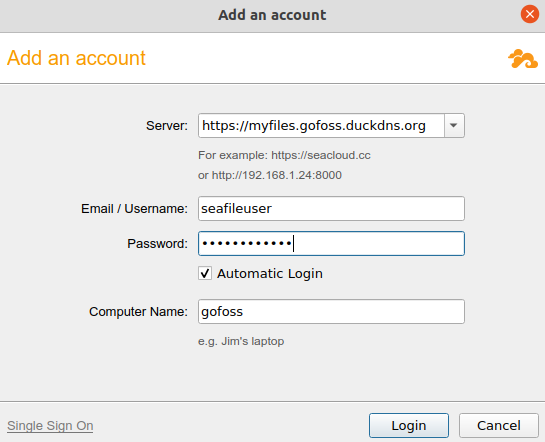 |
Show me the step-by-step guide for macOS
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Installation | Download & install the latest release of Seafile's Desktop Sync Client for macOS.  |
| Storage | Launch the Seafile client and select a local folder to be synched with the cloud. 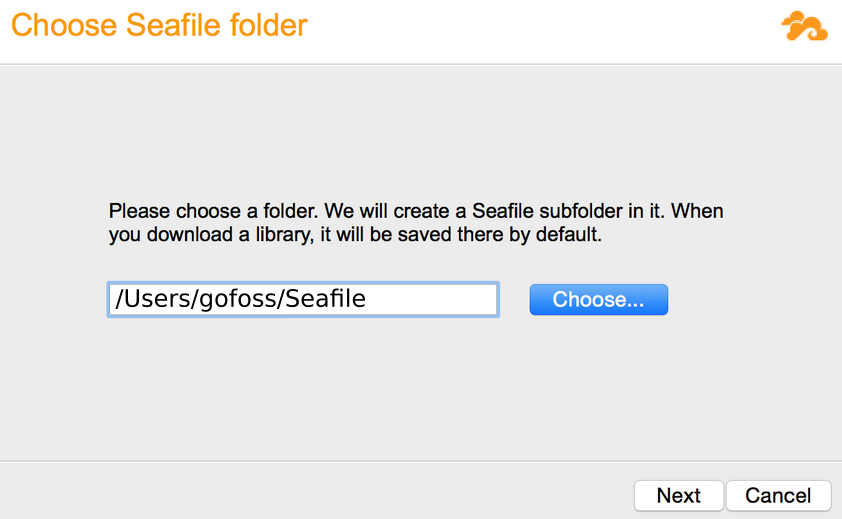 |
| Credentials | Provide the server name as well as user credentials. If enabled, also provide two-factor authentication.  |
Show me the step-by-step guide for Linux (Ubuntu)
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Signing Key | Open a terminal and add the signing key: sudo wget https://linux-clients.seafile.com/seafile.asc -O /usr/share/keyrings/seafile-keyring.asc |
| Repository | Add the repository to the apt source list for Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish):sudo bash -c "echo 'deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/seafile-keyring.asc] https://linux-clients.seafile.com/seafile-deb/jammy/ stable main' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/seafile.list"Then update the local apt cache: sudo apt update |
| Installation | Install the Seafile Syncing Client: sudo apt install -y seafile-gui |
| Storage | Launch the Seafile client and select a local folder to be synched with the cloud.  |
| Credentials | Provide the server name as well as user credentials. If enabled, also provide two-factor authentication.  |
SeaDrive¶
The SeaDrive Client works like a network drive. Users can access files on the server without prior synchronisation. Files can also be cached for offline use. SeaDrive is best suited to extend storage capacity of devices with limited disk space.
Show me the step-by-step guide for Windows
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Installation | Download & install the latest release of the SeaDrive Client for Windows.  |
| Virtual Drive | Launch the SeaDrive client and select a drive letter for the virtual drive. By default, S: will be used. |
| Credentials | Provide the server name as well as user credentials. If enabled, also provide two-factor authentication.  |
| File List | SeaDrive will fetch a list of all files & folders stored on the server, without actually downloading data. A notification will show once it's done. Cloud files can now be accessed via the Windows Explorer, just like any ordinary hard drive. 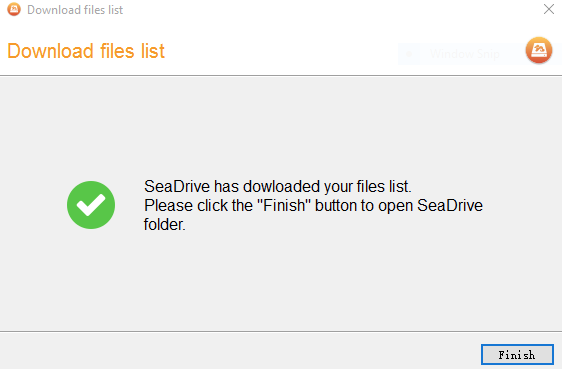 |
Show me the step-by-step guide for macOS
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Installation | Download & install the latest release of the SeaDrive Client for macOS.  |
| Virtual Drive | Launch the SeaDrive client and select a drive letter for the virtual drive. By default, S: will be used. |
| Credentials | Provide the server name as well as user credentials. If enabled, also provide two-factor authentication.  |
| File List | SeaDrive will fetch a list of all files & folders stored on the server, without actually downloading data. A notification will show once it's done. Cloud files can now be accessed, just like any ordinary hard drive.  |
Show me the step-by-step guide for Linux (Ubuntu)
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Signing Key | Open a terminal and add the signing key:sudo wget https://linux-clients.seafile.com/seafile.asc -O /usr/share/keyrings/seafile-keyring.asc |
| Repository | Add the repository to the apt source list for Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish):sudo bash -c "echo 'deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/seafile-keyring.asc] https://linux-clients.seafile.com/seadrive-deb/jammy/ stable main' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/seadrive.list"Then update the local apt cache: sudo apt update |
| Installation | Install the SeaDrive Client: sudo apt install -y seadrive-gui |
| Credentials | Launch the SeaDrive client and provide the server name as well as user credentials. If enabled, also provide two-factor authentication. After logging in, the virtual drive will be mounted in ~/SeaDrive. |
Mobile clients¶
Seafile is available on smartphones and tablets. Users can navigate through folders and upload, edit & download files. To save storage space, files are cached but not fully synchronised. Seafile's mobile apps also include a feature to automatically backup photos to the server. More detailed instructions below.
Show me the step-by-step guide for Android
Open F-Droid on your phone and install the Seafile application. Alternatively, install Seafile via the Aurora Store or Google's Play Store.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Server | Provide the address of the Seafile server, e.g. https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org (adjust accordingly). |
Provide the email address of the Seafile user, e.g. seafileuser@gofoss.net (adjust accordingly). | |
| Password | Provide the password of the Seafile user. |
| Token | If two-factor authentication is enabled, enter the token generated by andOTP on your phone. |
Show me the step-by-step guide for iOS
Install Seafile's file sharing app via the App Store.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Server | Provide the address of the Seafile server, e.g. https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org (adjust accordingly). |
Provide the email address of the Seafile user, e.g. seafileuser@gofoss.net (adjust accordingly). | |
| Password | Provide the password of the Seafile user. |
| Token | If two-factor authentication is enabled, enter the token generated by andOTP on your phone. |

Add users¶
Seafile differentiates between two user types:
-
Administrators have full access to Seafile. They can add, edit and remove files & folders as well as users. In addition, administrators can maintain and update the website. In our example, the administrator
seafileadminwas created during the installation of the Seafile server. -
Users can be added by administrators, but have limited access to Seafile. They can only manage files & folders if they have the right permissions.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Browse to https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org and log in as administrator, e.g.seafileadmin@gofoss.net (adjust accordingly). |
| Step 2 | Navigate to System Admin ‣ Users ‣ Add user. |
| Step 3 | Provide a user name, as well as a strong, unique password. Then click on Submit. |
Show me the 2-minute summary video
The system administrator logs into the Seahub web interface to add the users Georg, Tom and Lenina.
Admins & users need a VPN access
All users must be connected to the server via VPN to access Seafile.

Two factor authentication¶
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an optional feature to further increase security of file sharing programs. If enabled, logging into Seafile requires a password as well as a 6 digit code generated by an app on the user's phone. We recommend using andOTP, which can be installed from F-Droid.
Show me the step-by-step guide
First, Seafile's administrator needs to enable 2FA:
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Log into Seafile's web interface https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org as seafileadmin@gofoss.net (adjust accordingly). |
| Step 2 | Navigate to System Admin ‣ Settings ‣ Passwords. |
| Step 3 | Enable two factor authentication for all users. |
Next, each user needs to configure 2FA. Start with the Seafile administrator, and repeat for each user account set up subsequently:
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Log into Seafile's web interface https://myfiles.gofoss.duckdns.org. |
| Step 2 | Navigate to Settings. |
| Step 3 | Enable two factor authentication. |
| Step 4 | Open andOTP on the user's phone. |
| Step 5 | Scan the displayed QR code with andOTP. |
| Step 6 | Enter the 6 digit code generated by andOTP into Seafile's web interface. |
| Step 7 | Store the list of backup tokens provided by Seafile. They allow to recover access to Seafile without andOTP. |
Show me the 2-minute summary video

Add libraries, files & folders¶
Seahub enables users to create new libraries, files and folders via the browser. Users can also upload files and folders to existing libraries.
Show me the 2-minute summary video
Georg logs into the Seahub web interface to create a library with pictures from his hiking trip with Lenina. Tom also logs into the Seahub web interface to upload an essay on "Politics and the English Language", written by George Orwell in 1946.
Users can create new libraries or upload files and folders to existing libraries via Seafile's Syncing client. Instructions are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Create a new library | Open the Syncing client, click on Select and browse to the local folder you want to sync with the server. Alternatively, drag & drop the local folder to the designated area. Next, provide a name for the new library, and specify whether or not it should be encrypted with a password. 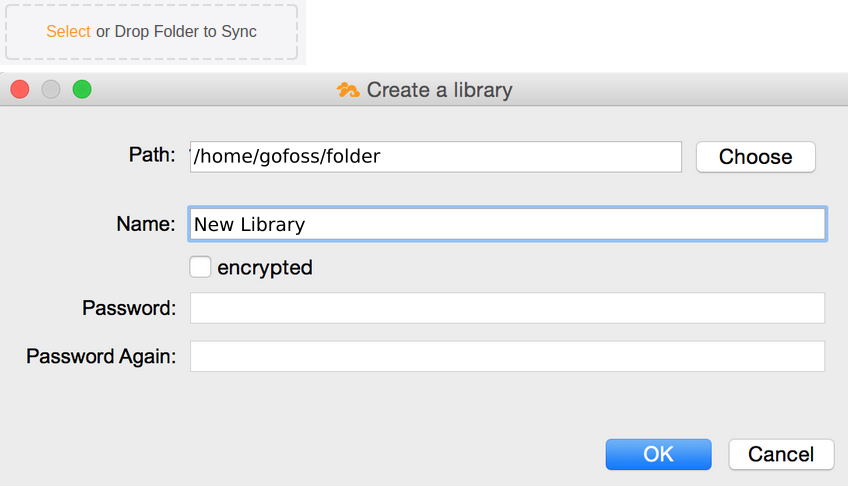 |
| Add files & folders to an existing library | Use the device's file manager. Navigate to the synchronised folder and add files & folders as required. Changes will be synchronised to the Seafile server, as well as any connected devices. |
SeaDrive works like a network drive. Users can directly create new or add existing libraries, files and folders from the device's file manager. For more details, refer to Seafile's User Manual describing the specificity of SeaDrive version 1 as well as SeaDrive version 2.

Sync data¶
Seafile works with so-called libraries, which contain the actual files and folders. The Syncing client makes sure that any local change to a library is mirrored to the Seafile server and other connected devices, and the other way round. Instructions on how to sync libraries are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Sync a library | Open the Syncing client and right click on the library. Then, select the menu entry Sync this library. All files and folders will be downloaded from the server to the local storage. From now on, any modification to local files will be mirrored to the server, and vice versa.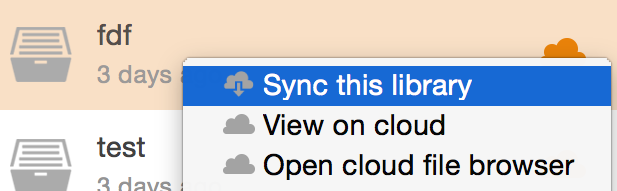 |
| Unsync a library | To stop syncing a library, right click and select the menu entry Unsync. Modification to local files will no longer be mirrored to the server, and vice versa. |
| Cloud File Browser | The Syncing client provides a so-called Cloud File Browser. It allows users to access and modify files directly on the server, without prior synchronisation. Right click on an (unsynced) library and select the menu entry Open Cloud File Browser. 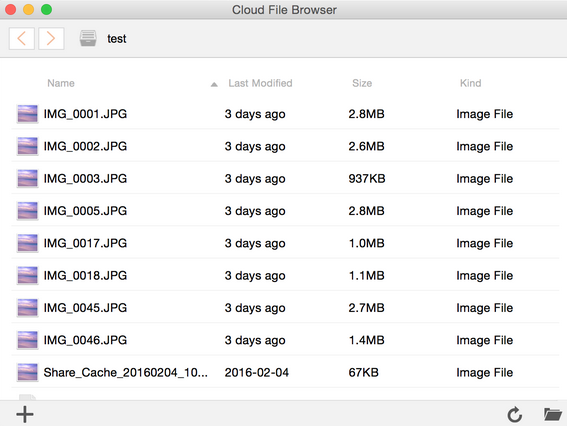 |
| Sync sub-folders | To avoid syncing large libraries, it's possible to sync specific sub-folders only. Right click on the library, select the menu entry Open Cloud File Browser, right click on the sub-folder and select the menu entry Sync this folder. 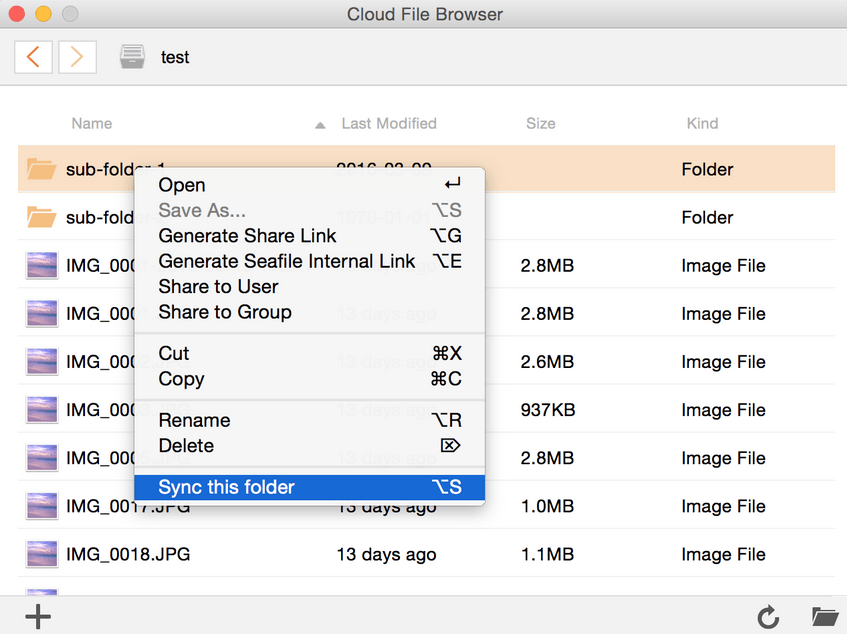 |
Show me the 1-minute summary video
Georg uses the Seafile Syncing client to synchronise his hiking pictures to his workstation. He then accesses the local copy of his pictures and moves them to a newly created folder labelled "holidays". These local changes are immediately mirrored to the Seafile server, as well as any other connected device. When Georg logs back into the Seahub web interface, the new "holiday" folder appears.
The SeaDrive client works like a network drive. Users can directly access files stored on the Seafile server, without prior synchronisation. Instructions on how to use SeaDrive are outlined below.
Tell me more about the sync status
Windows Explorer displays various icons to indicate the sync status of files and folders.
| State | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud-only |  | This is the default state of files and folders. They are displayed in SeaDrive, but aren't actually downloaded to the local storage. |
| Synched |  | Once a user decides to access a file or folder, it will be downloaded to the local storage. |
| Partially synched |  | Folders containing both cloud-only and synched files are considered as partially synched. |
| Locked by others | 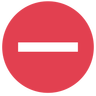 | Files locked by other users can only be opened in read-only mode, but not modified, deleted or renamed. |
| Locked by me | 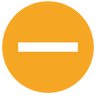 | A file or folder locked by its owner can't be modified by others. |
| Read-only | 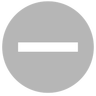 | Files or folders shared in read-only mode with a user can be opened, but not modified, deleted or renamed. |

Share files¶
Anyone with a public share link and a working VPN connection can access shared files & folders on the server. No Seafile account or login is required. Share links can be protected by a password, set to expire after a certain time or restrict file permissions. Instructions on how to create share links are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Navigate to the file or folder to be shared. |
| Step 2 | Hover over the file or folder and click on the Share icon. |
| Step 3 | Click on the Share Link tab in the pop-up window. |
| Step 4 | Click on the Generate button to create the share link. |
| Step 5 | Optionally, set a password, expiration time or permissions. |
| Step 6 | Share the link with others by email, messenger, and so on. |
Anyone with a public upload link and a working VPN connection can upload files & folders to the server. No Seafile account or login is required. Upload links can be password protected. Instructions on how to create upload links are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Navigate to the folder to which files are to be uploaded. |
| Step 2 | Hover over the folder and click on the Share icon. |
| Step 3 | Click on the Upload Link tab in the pop-up window. |
| Step 4 | Click on the Generate button to create the upload link. |
| Step 5 | Optionally, set a password. |
| Step 6 | Share the link with others by email, messenger, and so on. |
Libraries, files & folders can be shared with other Seafile users or groups. To access shared files, they need a working VPN connection, a Seafile account, and the right access permissions. Instructions on how to share libraries, files and folders with other Seafile users are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Navigate to the library or folder you want to share with other Seafile users. |
| Step 2 | Hover over the library or folder and click on the Share icon. |
| Step 3 | Click on the Share to user or Share to group tab in the pop-up window. |
| Step 4 | Select users or groups and click on the Submit button. |
| Step 5 | Set permission on the shared files & folders, such as read-write, read-only, online read-write or online read-only. |
Show me the 2-minute summary video
Share Links: Tom wants to share Orwell's essay with a friend from the book club. This friend can connect to the server via VPN, but doesn't have her own Seafile account. Tom therefore logs into the Seahub web interface to send her a share link, which expires after a week.
Share with Seafile users: Georg wants to share his hiking trip pictures with Lenina. Lenina can connect to the server via VPN, and owns a Seafile account. Georg therefore logs into the Seahub web interface and shares the "holidays" folder with Lenina, in "read-only" mode.
Upload Links: Georg needs to collect some work documents from a colleague. This colleague can connect to the server via VPN, but doesn't have his own Seafile account. Georg therefore logs into the Seahub web interface, creates a new library called "work", and sends an upload link to his colleague.

Restore files¶
Seafile automatically tracks the modification history of all files, folders and libraries. It keeps a backup of old file versions, as well as snapshots of folder and library structures for a predefined period of time. Files, folders or entire libraries can be restored to previous states in case of an accidental deletion or faulty operation.
The retention period defines for how long Seafile keeps file versions or library snapshots. It can be configured separately for each library, instructions are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Log into the Seahub web interface. Click on My Libraries in the navigation panel. |
| Step 2 | Hover the cursor over the library. |
| Step 3 | Click on History Setting. |
| Step 4 | Define the length of the retention period. |
Instructions on how to restore previous versions of a file are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Log into the Seahub web interface. Navigate to the folder containing the file. |
| Step 2 | Hover the cursor over the file. |
| Step 3 | Click on History. |
| Step 4 | Download, restore, or view any older version of the file. For text files, the content of two versions can be compared. Note that older versions of a file cannot be viewed if they exceed the retention period. |
Instructions on how to restore deleted files or folders from the trash bin are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Log into the Seahub web interface. Navigate to the parent folder containing the deleted file or folder. |
| Step 2 | Click on the trash icon in the library operation bar. |
| Step 3 | Restore the deleted file or folder from the list. Note that files and folders cannot be restored if they have been deleted before the retention period. |
Library snapshots allow to list and restore older versions of an entire library, including its complete file and folder structure. Instructions are outlined below.
Show me the step-by-step guide
| Instructions | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Log into the Seahub web interface. Navigate to the library. |
| Step 2 | Click on the History button in the top bar. |
| Step 3 | Select a previous state of the library and click on View snapshot. |
| Step 4 | Download, restore, or view any older version of a file or folder. If you're the library's owner, you can restore the entire library to its previous state. Note that library snapshots cannot be accessed if they exceed the retention period. |
Show me the 2-minute summary video
Retention period: In order to save storage space, Georg instructs Seafile to keep older versions of his pictures for 2 months only.
Library snapshots: Georg also wants to revert to the folder structure which was in place before he created the "holidays" folder. He therefore restores an older snapshot of the library.
Trash bin: Tom restores Orwell's essay from the trash bin, after having deleted it inadvertently.

Encrypt files¶
Seafile provides client-side end-to-end encryption. Libraries can be encrypted with a password, limiting access to authorised users only. No one else can access the content of encrypted libraries, not even the Seafile administrator. Note however that encrypted libraries only encrypt file contents, not folder and file names.
Show me the 1-minute summary video
Tom is working on a sensitive project. He creates an encrypted library to keep his project documents safe.

Upgrade¶
Seafile's upgrade process is mainly manual and things can go wrong. Don't take any chances, sync all your libraries to a device and back up your data!
Make sure to read Seafile's upgrade instructions, as well as the detailed upgrade notes. Below you'll find a walkthrough for a major version upgrade.
Walk me through the upgrade process
For the purpose of this tutorial, let's assume you want to upgrade from version 7.0.1 to version 8.0.1. This is called a "major version upgrade". Note that "minor version upgrades", for example from 7.0.1 to 7.1.1, work similarly.
Start by reading the upgrade notes, which contain specific settings or changes that must be applied before or during the upgrade.
Download and extract the latest release of Seafile's Server for Linux. In this example, it would be version 8.0.1. Make sure to adjust the version number accordingly:
sudo wget -4 https://download.seadrive.org/seafile-server_8.0.1_x86-64.tar.gz
sudo tar -xvf seafile-server_*
sudo mv seafile-server-* /var/www/seafile
sudo mv seafile-server_* /var/www/seafile/installed
Set the right permissions:
sudo chown -R seafileadmin:seafileadmin /var/www/seafile
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/seafile
Verify everything is in place:
sudo ls -al /var/www/seafile
The directory layout should look something like:
/var/www/seafile/
-- ccnet
-- conf
-- installed
-- logs
-- pids
-- seafile-data
-- seafile-server-7.0.1
-- seafile-server-8.0.1
-- seafile-server-latest
-- seahub-data
Shutdown the Seafile server:
sudo systemctl stop seafile
sudo systemctl stop seahub
Get a list of available upgrade scripts:
sudo ls -al /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_*
The terminal should print something like:
...
/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_6.0_6.1.sh
/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_6.1_6.2.sh
/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_6.2_6.3.sh
/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_6.3_7.0.sh
/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_7.0_7.1.sh
/var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_7.1_8.0.sh
...
Now, run the required upgrade script(s), starting from your current Seafile version and working your way up to the latest version. In this example:
- we first have to run the script
upgrade_7.0_7.1.shto upgrade from version 7.0.1 to version 7.1.x - we then have to run the script
upgrade_7.1_8.0.shto upgrade from version 7.1.x to version 8.0.1
Start with the first upgrade script:
sudo bash /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_7.0_7.1.sh
The terminal should prompt something similar to:
-------------------------------------------------------------
This script would upgrade your seafile server from 7.0 to 7.1
Press [ENTER] to continue
-------------------------------------------------------------
Updating seafile/seahub database ...
[INFO] You are using MySQL
[INFO] updating seahub database...
Done
migrating avatars ...
Done
updating /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest symbolic link to /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-7.1.0 ...
Now the next upgrade script:
sudo bash /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1/upgrade/upgrade_7.1_8.0.sh
The terminal should prompt something similar to:
-------------------------------------------------------------
This script would upgrade your seafile server from 7.1 to 8.0
Press [ENTER] to continue
-------------------------------------------------------------
Updating seafile/seahub database ...
[INFO] You are using MySQL
[INFO] updating seahub database...
Done
migrating avatars ...
Done
updating /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-latest symbolic link to /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-8.0.1 ...
Finally, start up the Seafile server again:
sudo systemctl start seafile
sudo systemctl start seahub
If all went well, Seafile should be running, and its status should show "Active":
sudo systemctl status seafile
sudo systemctl status seahub
Optionally, if the new version works fine, you can remove the previous version:
sudo rm -rf /var/www/seafile/seafile-server-7.0.1

Support¶
For further details, refer to Seafile's server manual or request support from the Seafile community.